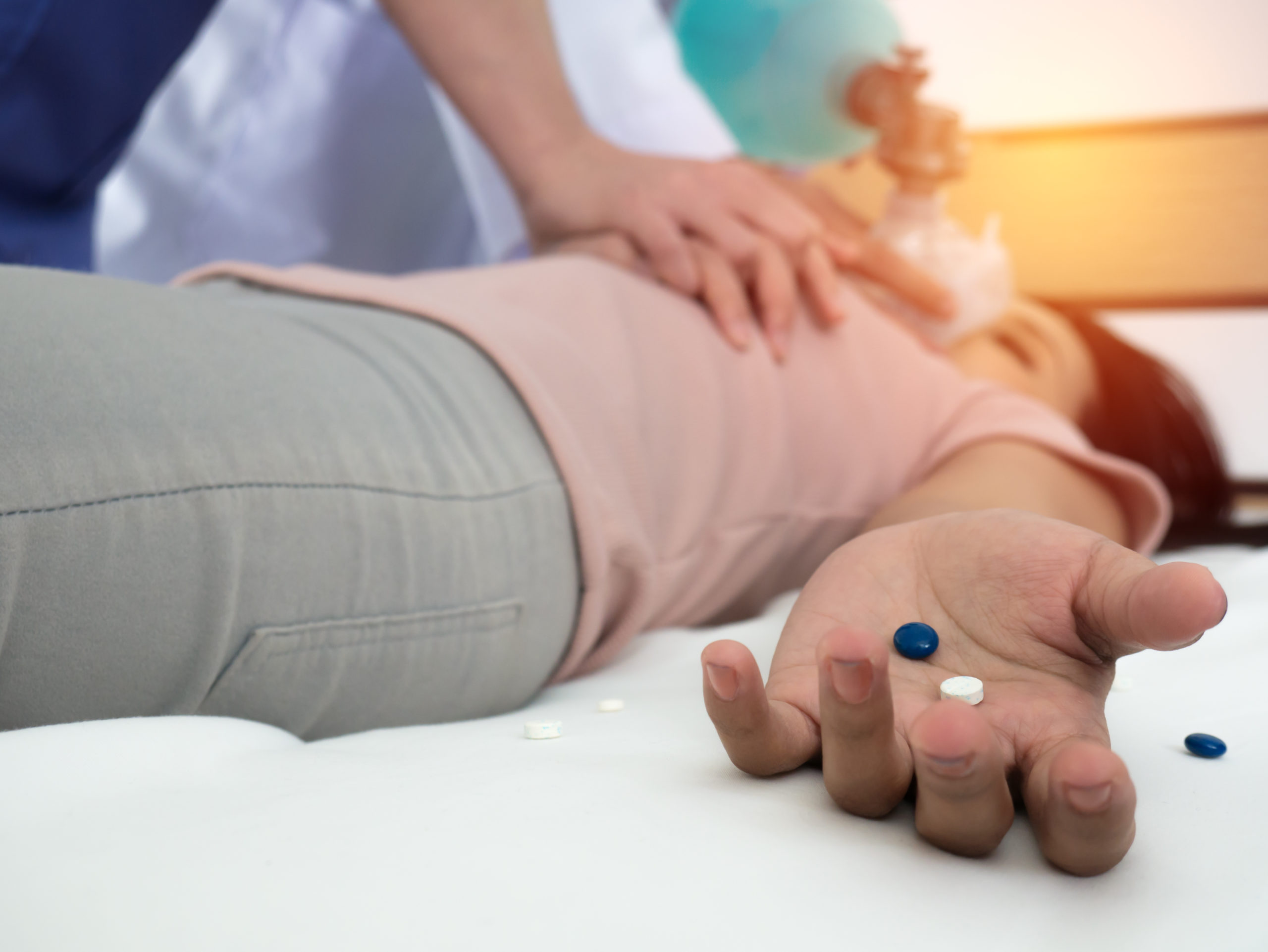
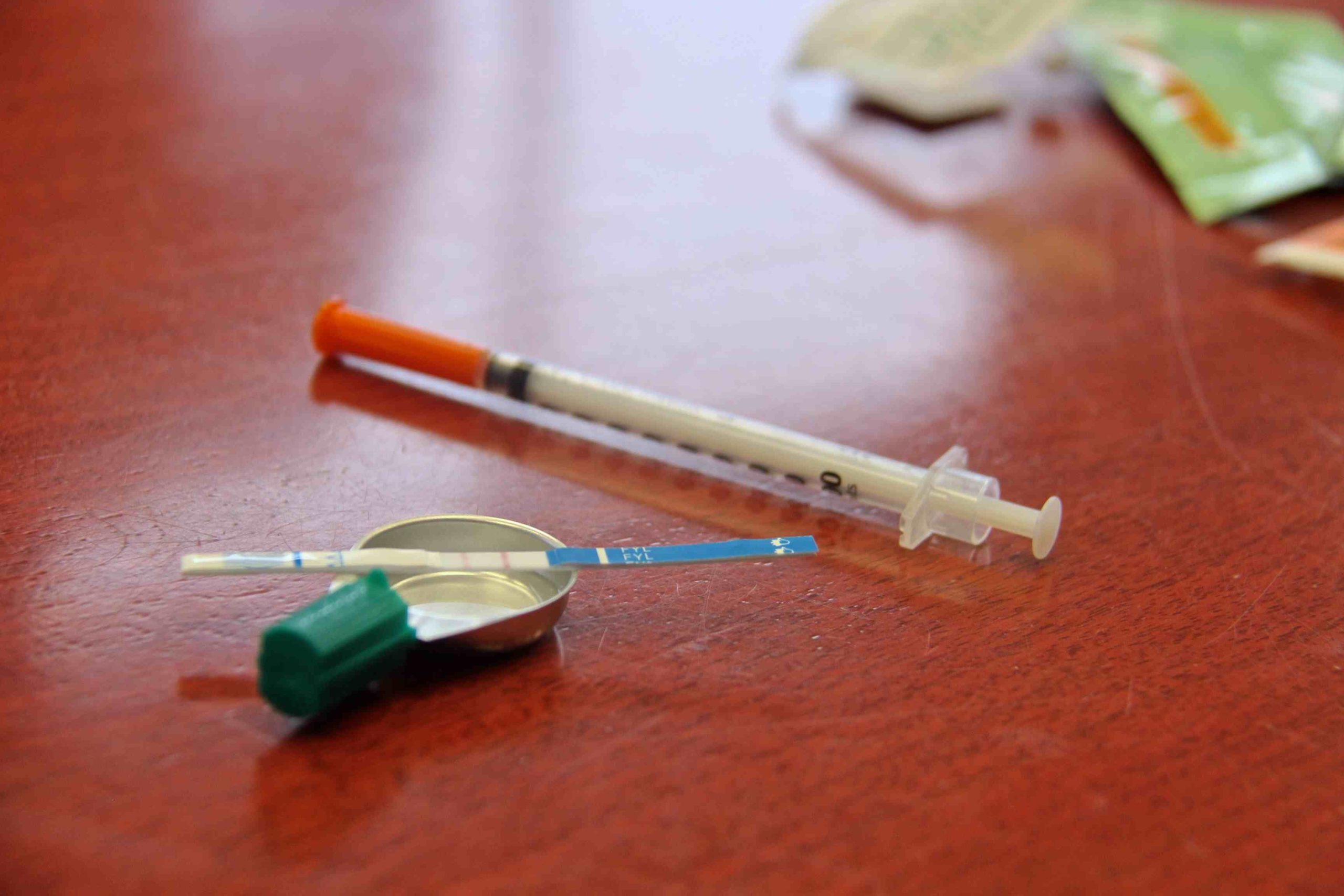
Research indicates that there is often a reluctance among those witnessing an overdose to summon emergency assistance from law enforcement or other first responders out of fear of arrest for drug possession or other charges. In an effort to reduce this fear and to encourage overdose witnesses to seek help, state policymakers developed Good Samaritan laws specific to drug overdoses. The purpose of these laws is to prioritize the overdose victim’s safety over arresting drug users by granting limited protection from criminal liability to persons seeking medical assistance and, in most cases, to the overdose victim. This document (1) provides a singular resource for each jurisdiction's laws; (2) allows for a comparison of these laws between jurisdictions; and (3) identifies and highlights interesting provisions.
...